testicular torsion test cryp|testicular torsion physical examination : maker Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and vomiting, past trauma, a tender testicle, an abnormal testicular lie (i.e., elevated or transverse), and.
Free spins bonuses 🔍 Key info. Our checklist highlights the key metrics of free spins bonuses. Use it to help find the right offer and enjoy your free spins on online slots. ⭐ Best free spins .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Scopri la panoramica dei nostri fantastici giochi nuovi, inclus.
What is Prehn’s sign? Prehn's sign is a clinical finding that helps clinicians determine whether testicular pain is caused by epididymitis or testicular torsion. A positive Prehn's sign, characterized by pain relief from the . Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Definition: Twisting of the spermatic cord leading to decreased blood flow to the testicle resulting in ischemia, infarction and potentially, tissue necrosis. Epidemiology: Most . Ultrasound is a sensitive and specific test for the evaluation of testicular torsion. Early urology involvement is crucial to avoid testicular loss. The use of color flow is essential in .
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; .
Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and vomiting, past trauma, a tender testicle, an abnormal testicular lie (i.e., elevated or transverse), and.
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical .
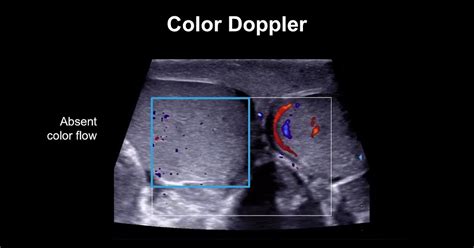
Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or . Diagnosis of testicular torsion is based on the finding of decreased or absent blood flow on the ipsilateral side. Treatment involves rapid restoration of blood flow to the affected testis. The.
Scrotal complaints are relatively common in the emergency department, comprising at least 0.5% of all emergency department visits. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to evaluate the .[1,2] Testicular torsion is a urological emergency that affects any age group but most common in the second and third decades of life. Pentyala et al. [6] reported a peak age range of 12-18 years .
↑ Blaivas, M, et al. Emergency evaluation of patients presenting with acute scrotum using bedside ultrasonography. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2001; 8(1):90-93. ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8. ↑ Gordon J, Rifenburg RP. . Spermatic Cord .
2 Contents 1 Foreword 2 2 Summary of key pathway components 3 3 Testicular torsion pathway 3 3.1 Raising awareness 4 3.2 Referral pathways 4 3.3 Assessment, including TWIST score & ultrasound 5 3.4 Surgery 6 3.5 Follow up 6 3.6 Revalidation & maintaining skills 6 4 Patient experience 7 5 Audit points & areas for further research 8 6 Resources & further information 8Testicular torsion in young boys and teen boys occurs when the testicles are not completely attached in the scrotum. This lets the testicles move more freely and twist. . He may also have tests, such as an ultrasound. This is a painless imaging test that uses sound waves to see the scrotum and testicles and check blood flow. Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. . Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic Test for Testis Torsion in Pediatric Acute Scrotum: A Prospective Comparison to Gold Standard Diagnostic Test Study. J Urol .
The main symptom of testicular torsion is extreme abdominal pain. Your dog might also be: Lethargic; Have increased drinking; Vomiting ; Testicular tumors (cancer) are more common than a twist, and dogs with retained testicles (one or two) have a higher chance of having cancer of the testicle. Testes with a tumor often change shape and consistency.Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours . See a doctor right away if you think you have .Cryptorchidism, also known as undescended testis, is the failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum.The word is from Ancient Greek κρυπτός (kryptos) 'hidden' and ὄρχις (orchis) 'testicle'. It is the most common birth defect of the male genital tract. [1] About 3% of full-term and 30% of premature infant boys are born with at least one undescended testis. [2]
Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicle and preserving future fertility. . Laboratory tests are unlikely to be of consequence, as no single test .23YOM, Test Cyp IM, Hypogonadism, testicular torsion, Extremely high E2 . Been talking test for a year. Started at 170lbs 5’ 9”. Now am 220lbs. Water retention. Blood pressure 160/90. ED problems. Suspect high E2. Has blood work done, E2 is 300ng/dL (15-30). Anastrozole .25 x2 week. Not cutting it. Introduction. Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord and its contents twists within the tunica vaginalis, compromising the blood supply to the testicle.. Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency, as without treatment the affected testicle will infarct within hours.Whilst theoretically it can occur at any age, peak incidence is in neonates and .The most common signs of cryptorchidism are male marking behavior (spraying), male cat-associated odors, and aggression. Cats appear to have fewer incidences of testicular cancer and complications associated with cryptorchidism than dogs. One complication of cryptorchidism is spermatic cord torsion (twisting onto itself). If this occurs, there .
On physical exam, the scrotum is blue and firm with some erythema. Transillumination test is negative. Doppler ultrasound shows absent blood flow. The neonate is immediately sent to hospital for surgery. Introduction. . Testicular Torsion Renal - Testicular Torsion; Listen Now 15:31 min. 9/6/2021. 48 plays. 0.0 (0) Testicular torsion is a very serious condition and is considered a medical emergency. Rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord can cause obstruction of the arterial blood flow to the testicle, as well as the venous .American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, .Testicular torsion can occur at any age but commonly occurs soon after birth or between the ages of 12–18 years with a peak in incidence at age 13–14 years. . With regards to the intraoperative bleeding test, all patients with grade 3 bleeding (major bleeding that requires multiple hemoclips and sessions of hemocoagulation) required .
Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and definitive management are the keys to avoid testicular loss. All prepubertal and young adult . References. Ben-Israel T et al. Clinical predictors for testicular torsion as seen in the pediatric ED. Am J Emerg Med 2010; 28:786-789.PMID: 20837255 Sidler D et al. A 25-year review of the acute scrotum in children.
Testicular torsion is characterized by sudden-onset unilateral testicular pain, which may radiate to the lower abdomen, with nausea and vomiting. Clinical findings include a high-riding. testis. with an absent . cremasteric reflex. Imaging with .
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become . Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies. Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage. . Tests that can be used to .Cryptorchidism is a condition in which a testicle has not descended to its proper position in the scrotum. It is the most common genitourinary malformation in male children and affects 45% of .
A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).Testicular torsion can occur at any time – e.g. while sleeping, sitting on the couch, or after activity and trauma. Rapid growth of the testicles during puberty is also a risk factor. Who is at risk of testicular torsion? Most cases are between the ages of 12 and 18, but testicular torsion can occur at any age. Signs and symptomsTesticular torsion. Testicular torsion is a painful condition in which your testicular blood supply (the spermatic cord) twists and cuts off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion affects about 1 in 4,000 people under the age of 25. At what age should an orchiopexy be done?
tft blood test bottle colour
WEBColumns 1, X and 2 serve for average/biggest Super League 2021/2022 betting odds offered on home team to win, draw and away team to win the Super League 2021/2022 match. The top line of upcoming matches table (Basketball - Russia - Super League 2021/2022) lets you click-through to higher categories of Odds Portal betting odds .
testicular torsion test cryp|testicular torsion physical examination